If you’re using Google Workspace or considering Workspace for your organization, you may have questions about Google Workspace security in your mind.
After all, company email and business documents (if you are leveraging Google Drive for cloud backup of local files) are stored in Google’s data centers.
Workspace security should be part of an extensive data security management approach.
As you’d expect, Google Workspace has multiple levels of built-in security.
Google Workspace Data Center Security
Google’s data center security is superior to that of most corporate networks. Google has hundreds of full-time security engineers, some of whom are leading experts in the field.
Data moving within Google’s data centers and to and from its data centers is encrypted using perfect forward secrecy. With perfect forward secrecy, breaking an encryption key would not do a hacker any good.
You can find Google Workspace security FAQs here.
As with many web applications that have hardened data center security, the easiest access point for an intruder may be via user login access.
Google Workspace User Access Security
Google provides multiple levels of native protection to prevent a dictionary attack.
What can users of Google Workspace do to make account access even more secure?
Use a unique, long password
By default, a Google Workspace password can be up to 100 characters long. Spaces within passwords are permitted, which means that password phrases can be used. A Google Workspace admin can increase the minimum required password length and the maximum possible password length.
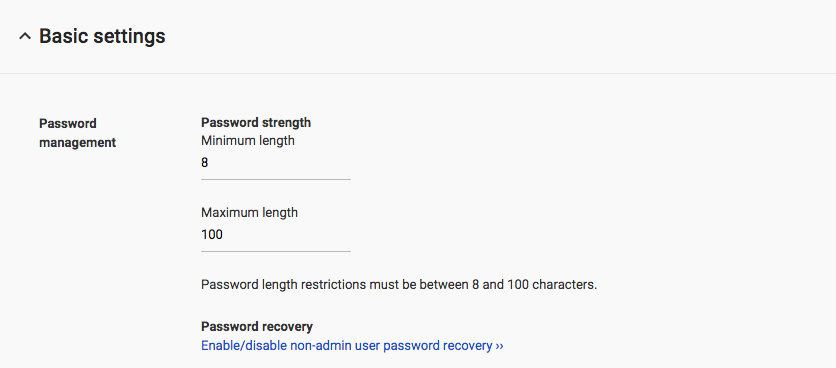
A randomly generated password phrase or “passphrase” is more secure and is easier to remember than a password such as T%e3$&1#.
You can use a site such as Use a Passphrase to generate passphrases. An example passphrase we generated is “swedish wide finish spectra”. The approximate crack time reported by Use a Passphrase is 57,384 centuries.
Keep a secure record of all passwords
Users should only keep a physical record of their Google Workspace password (and all their other passwords) in an encrypted password database such as 1Password.
In other words, users should avoid storing passwords in a spreadsheet, a document, or paper.
Enable Google 2-Step Verification
A Google Workspace administrator can enable Google 2-Step Verification (2SV).
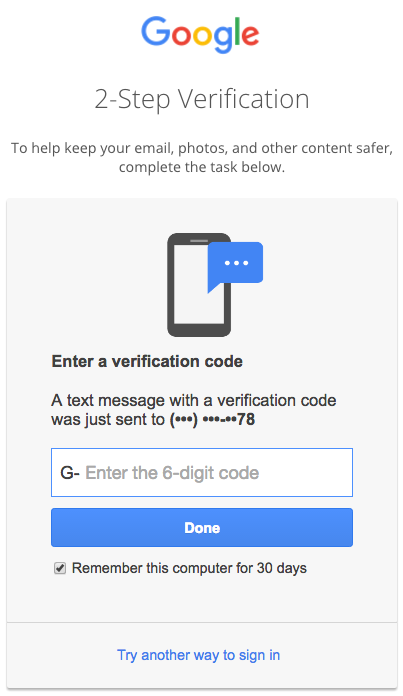
Once a Google Workspace administrator has enabled 2-Step Verification, users can enable one or more options for their account by going to My Account > Signing Into Google > 2-Step Verification.
Note: An administrator can enforce 2SV for all users.
Before 2SV is enforced, all users must be first enrolled in 2SV so they are not locked out of their accounts. Users can be placed in an exception group until they enable 2SV.
When a user logs in from an unfamiliar device or location, several verification options are available. These options are not mutually exclusive.
1. The user can enter a Google Verification Code texted to them.
According to Google, “As awareness of the potential vulnerabilities associated with SMS and voice codes has increased, some admins asked us for more control over the ability to use phone-based 2-Step Verification methods within organizations.” Because of this, admins can now disable SMS or voice codes as a 2SV option.
It has also been reported that Google Workspace accounts with 2SV legacy were breached with brute force attacks on legacy IMAP protocol.
In other words, using a passphrase makes sense even if 2SV is enabled.
2. If users install the Google app on their Android or iPhone, they can verify by simply answering “Yes” on their mobile device. This option is known as Google Prompt.
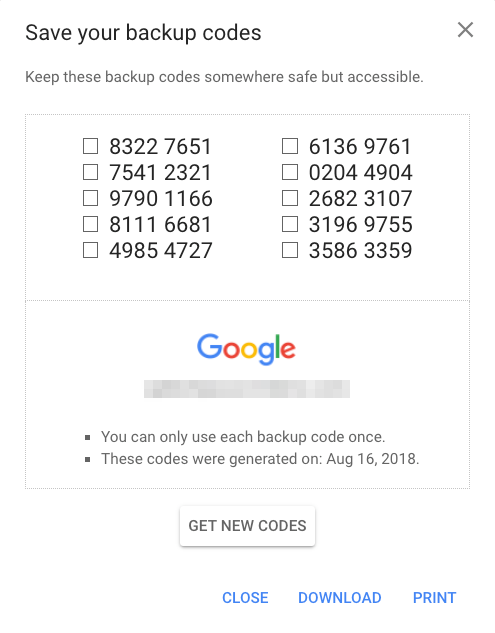
3. A user can generate and print out a list of one-time-use backup codes. These can be kept in a wallet, a locked drawer, or a safe.
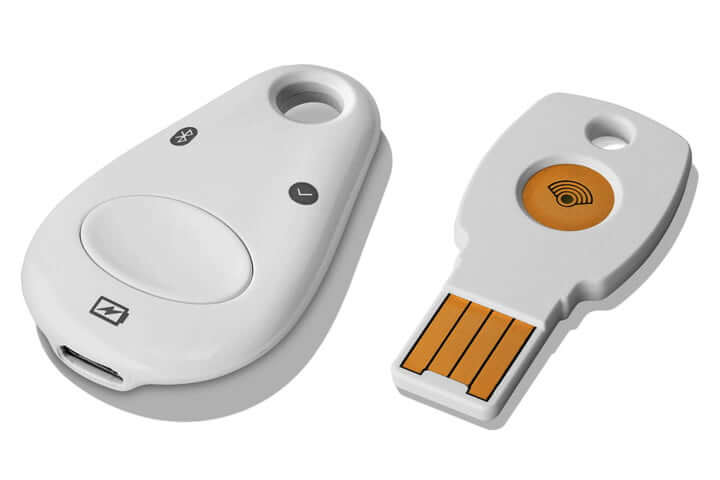
Use a Physical Security Key
Google’s Titan Security key is available in Google’s online store.
This is a physical key that can be kept on a key chain. It plugs into a computer’s USB port, and it is the best defense against phishing attacks.

In 2017, Google required all its employees to use a security key. Since then, not one employee account has been compromised.
Using a security key does not supersede the ability to use a verification code; it just provides an additional layer of security.
Enable enhanced email scanning and screening
A Workspace administrator can enable enhanced pre-delivery message scanning. This enables Gmail to help catch emails that previously may not have been identified as phishing.
This setting can be found in the admin console under Apps > Google Workspace > Gmail > Spam, Phishing, and Malware.
There are also advanced security settings for attachment protection, suspicious email protection for IMAP users, external images and links protection, and spoofing and authentication protection.
With some basic actions, admins and users can strengthen Google Workspace security.


